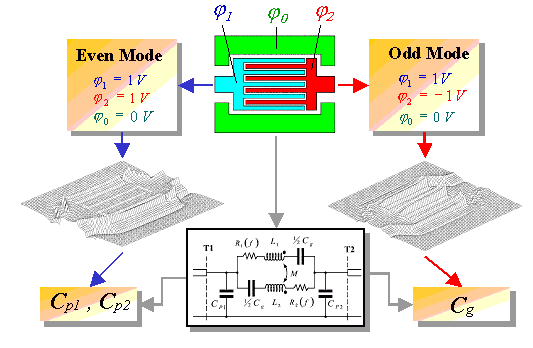
The calculation of capacitive model parameters is demonstrated here in case of an interdigitated capacitor. The procedure is shown in Figure 2-5. Two different potential configurations are used for the calculation of shunt capacitances Cp1 and Cp2 as well as the couple capacitance Cg. By the so called even mode simulation, the center lines and the fingers of the capacitor are set on the same potential of 1Volt whereas the ground planes are set to zero Volt. The solution of the Laplace´s equation leads to the field distribution on the metalization. The shunt capacitances Cp1 and Cp2 are calculated from the charge distribution on the conductors.