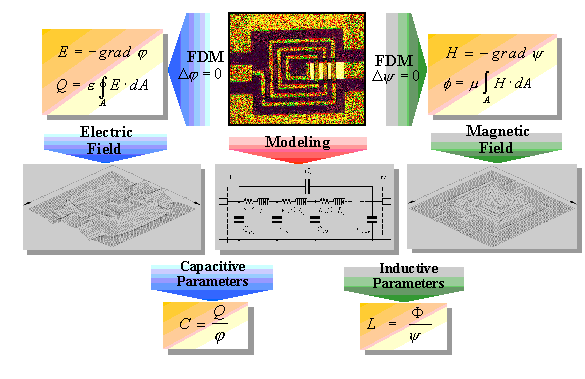
Figure 2-1. Field-theoretical modeling of coplanar structures used in COPLAN for ADS
| [close window] | [1 Introduction] |
The kernel of the simulation software is a field-theoretical modeling of elements in conjunction with the so called quasi-static Finite Difference Method (FDM) [2.1, 2.2]. An overview of the applied numerical method for the simulation of coplanar structures is shown in Figure 2-1.

The first modeling step is the chose of a suitable broadband equivalent circuit which is able to represent the physical characteristics of the structure in a wide frequency range. The model parameters are then determined by the calculation of the field distributions. For this, the structure is surrounded by a box of electric and magnetic walls and the box space is divided into elementary cells using a grid (discretization). The solution of the Laplace´s differential equation for all grid points leads to the electrical field distribution inside the box as well as the charge distribution on the metalization. This physical quantities are used together with the selected equivalent circuit in order to determine the capacitive model parameters.
In a similar way, the magnetic field distribution as well as the surface current distribution are calculated by solving the Laplace´s differential equation for the scalar magnetic potential. The inductive and resistive model parameters are then derived from the magnetic flux in slots and surface current on conductors.